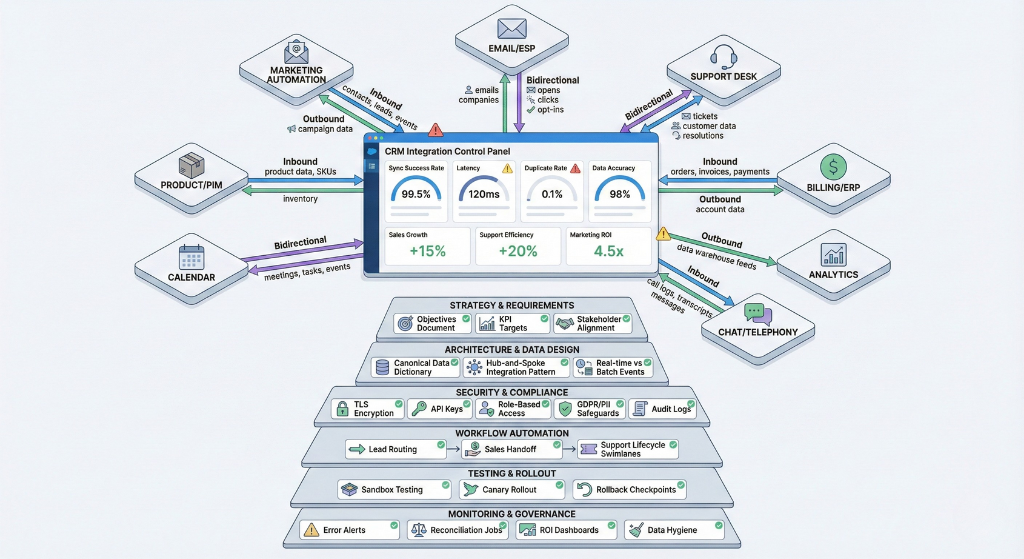
A practical, operational audit & planning framework to evaluate, design, and maintain CRM integrations. Use this checklist before, during, and after projects to reduce risk, ensure value, and keep systems reliable.
1. Strategy & Requirements Definition
Goal: make the integration deliver measurable business outcomes and avoid “shallow” syncs that add overhead without benefit.
Questions to answer (must-have outputs)
- Business objectives (documented): unified customer profile, sales automation, marketing automation, support-ticket sync, billing/ERP sync, analytics consolidation.
Deliverable: one-page Objectives Statement with success metrics. - Systems to integrate (inventory): email/ESP, marketing automation, support desk, billing/ERP, PIM, analytics, chat/comms, calendar, telephony/VOIP.
Deliverable: Integration Inventory (system name, owner, primary API, contact). - Data model & fields (canonical mapping): define which objects and fields flow (contacts, companies, deals, orders, tickets, events, product purchases). Specify direction (inbound/outbound/bidirectional).
Deliverable: Canonical Data Dictionary (field name, type, source system, direction, validation rules). - Data governance & compliance: ownership, roles, access policies, retention, consent capture, GDPR/CCPA implications.
Deliverable: Data Governance Matrix (roles, PII handling, retention). - Stakeholder alignment: sales, marketing, support, finance, IT agree on workflows and KPIs.
Deliverable: RACI + KPI list (lead response time, conversion rate, data accuracy, duplicate rate). - Success metrics: define primary KPIs and measurement windows (e.g., Lead response time reduction target within 90 days).
Deliverable: KPI dashboard spec.
Acceptance criteria before design
- Objectives signed off by stakeholders.
- Inventory & data dictionary completed.
- Compliance constraints documented.
2. Technical Compatibility & Integration Architecture
Goal: choose an architecture that scales and is maintainable.
Architecture choices & checks
- Connector options: confirm CRM offers open APIs / webhooks or pre-built connectors. If not, expect custom middleware / iPaaS.
Decision output: Use native connector → lower maintenance; custom middleware → greater control. - Integration pattern: point-to-point (simple, short-term), hub-and-spoke (scalable), or hybrid. Avoid unmanaged point-to-point as systems increase.
Deliverable: Architecture Diagram (systems, data flows, real-time vs batch). - Real-time vs batch: define which events need immediate sync (lead creation, payments, support tickets) and which can be batched (weekly reconciliations).
Deliverable: Event SLA table (event, required latency). - API readiness: confirm external systems expose stable APIs, webhooks, pagination, rate limits, field schemas. Document API versions and change policies.
Deliverable: API Capability Matrix. - Error handling & observability: design retry logic, dead-letter queues, error alerts, logging, and reconciliation jobs.
Deliverable: Integration Runbook (error codes, retry rules, alerts). - Data transformations: map data formats, normalize date/time, currencies, enums, and required/optional fields.
Deliverable: Transformation Rules (source→target conversions). - Deduplication & identity resolution: strategy for matching contacts (email, phone, external id), merge rules, and authoritative source per field.
Deliverable: Identity Resolution Policy.
Technical acceptance criteria
- Architecture diagram approved, real-time events identified, error handling documented, and mapping rules complete.
3. Security, Data Privacy & Compliance
Goal: protect customer data, meet regulatory requirements, and prevent unauthorized access.
Mandatory checks
- Secure transport: all API calls over HTTPS/TLS; no cleartext data.
- Access controls: least-privilege API keys, role-based access in CRM, separate creds per environment.
- PII handling: limit stored PII, encrypt sensitive fields at rest if required, document legal basis/consent for processing.
- Backups & recovery: scheduled backups, retention policy, restore validation, and sandbox copies for testing.
- Audit & logging: immutable logs of data changes and integration activity for audit trails.
- Vendor compliance: verify CRM and third-party tools’ certifications (ISO, SOC2, GDPR readiness).
- Data minimization: only sync fields necessary for business processes.
Deliverables
- Security checklist (keys, vaults, rotation cadence).
- Compliance register (regulations applicable and mitigation actions).
- Backup & restore SOP.
4. Workflow Design & User Adoption Considerations
Goal: ensure the integration automates valuable workflows and users adopt the new system.
Workflow design steps
- Map end-to-end workflows: lead capture → scoring → assignment → nurture → handover → support ticket lifecycle. Use swimlane diagrams showing system responsibilities.
Deliverable: Workflow Maps (with system owners). - Phased rollout: prioritize core flows (contact sync, lead assignment) then expand (advanced automation, enrichment). Avoid big-bang.
Deliverable: Phase Plan (MVP + later phases). - Training & documentation: role-based guides, quick-reference cards, and recorded walkthroughs.
Deliverable: Training curriculum + documentation portal. - User acceptance criteria: define success for users (e.g., reduction in manual data entry by X%).
Deliverable: UAT checklist. - Avoid over-automation: preserve manual override points and human-in-the-loop for edge cases.
5. Testing, Quality Assurance & Rollout Strategy
Goal: verify correctness, avoid data loss, and be able to rollback.
Testing phases & cases
- Sandbox tests: full test-suite in isolated environment using anonymized production-like data.
- Test cases to cover: create/update/delete flows, duplicate detection, bulk import, webhook retries, permission boundaries, consent flows, GDPR delete requests.
- Edge cases: partial failures, partial payloads, malformed data, rate-limited responses.
- Load tests: for high-volume events (e.g., marketing send spikes) and real-time bursts.
- Security tests: penetration / API fuzzing, access token misuse scenarios.
Rollout strategy
- Canary rollout: enable integration for a subset of users/segments first.
- Monitoring during rollout: sync success rate, error rate, duplicate counts, latency, and business KPIs.
- Rollback plan: automated snapshot restore or targeted reversal process for specific data types.
- Post-launch audits: scheduled reconciliation jobs for first 30/90 days.
Deliverables
- Test plan + test cases, UAT signoff checklist, rollout runbook, rollback SOP.
6. Measuring ROI & Ongoing Governance
Goal: quantify benefits and keep integrations healthy.
Metrics to track
- Operational efficiency: hours saved, reduction in manual tasks, fewer data-entry errors.
- Sales performance: lead response time, conversion rate, sales cycle length.
- Support metrics: first response time, resolution time, ticket volume trends.
- Data quality metrics: duplicate rate, sync failure rate, missing-mandatory-field incidents.
- Financial impact: reduction in churn, increase in ARPA (average revenue per account), uplift in LTV.
Governance practices
- Periodic data hygiene: scheduled dedupes, stale-contact archiving, field audits.
- Integration lifecycle management: document connectors, API versions, scheduled dependency reviews.
- Change control: process for schema changes, new connectors, or field deprecations.
- Alerting & SLAs: SLOs for sync latency and error budgets; alert routing to owners.
- Documentation & handover: living docs for every integration, owner contact, and runbooks.
Deliverables
- ROI measurement plan (KPIs, baseline, cadence).
- Integration governance playbook (roles, change process, audit schedule).
Common Risks & How to Mitigate Them (quick reference)
- Shallow integrations (contact sync only) → mitigate by defining business workflows and mapping required objects before building.
- Point-to-point complexity → use hub-and-spoke or iPaaS for scale.
- Bad data hygiene → include deduplication and validation in pipeline; schedule cleanup.
- Security/compliance gaps → encrypt, limit PII, rotate keys, and audit regularly.
- Poor adoption → phase rollout, train users, preserve manual overrides.
Final Operational Checklist (one-page)
- Objectives Statement approved.
- Integration Inventory and Canonical Data Dictionary complete.
- Architecture Diagram & Event SLA defined.
- Security & Compliance checklist passed.
- Sandbox tests and UAT passed.
- Rollout plan with canary and rollback procedures.
- Monitoring & reconciliation jobs scheduled.
- ROI dashboard and governance playbook ready.
